Connect With Our Team
Knowledge of the differences between residential and commercial solar panels is very important when one is thinking of adopting solar energy. Although both systems utilize the same source of renewable energy, the comparison of residential vs commercial solar panels shows that the dimensions of design, installation, financing, and performance qualities will greatly affect the decision involved in making investments and their future implications.
Fundamental Differences in Solar Panel Systems
The most significant distinctions between residential and commercial solar go way beyond just scale differences. The systems are designed to have different and clear energy requirements, installation conditions and running conditions that mould their entire design and execution.
The residential-scale solar panel is provisionally set up for single-family, townhouses, and small multi-unit residential buildings. The average home solar system capacities are between 3–15 kilowatts and are aimed at substituting solar electricity for home usage whilst taking a comprehensive approach to aesthetic compatibility on the existing roof facilities. These solar panels for home applications ensure optimal performance and long-term cost savings.
Commercial solar panels serve businesses, industrial facilities, schools, hospitals, and large-scale solar installations. Such systems are usually larger than 100 kilowatts and optimize their interest in generating as much power as possible, efficiency, and financial returns in the time span rather than beauty. Commercial solar power solutions are typically offered by experienced commercial solar panel companies or commercial solar companies that tailor systems to fit industrial and business energy needs.
Size and Scale Distinctions
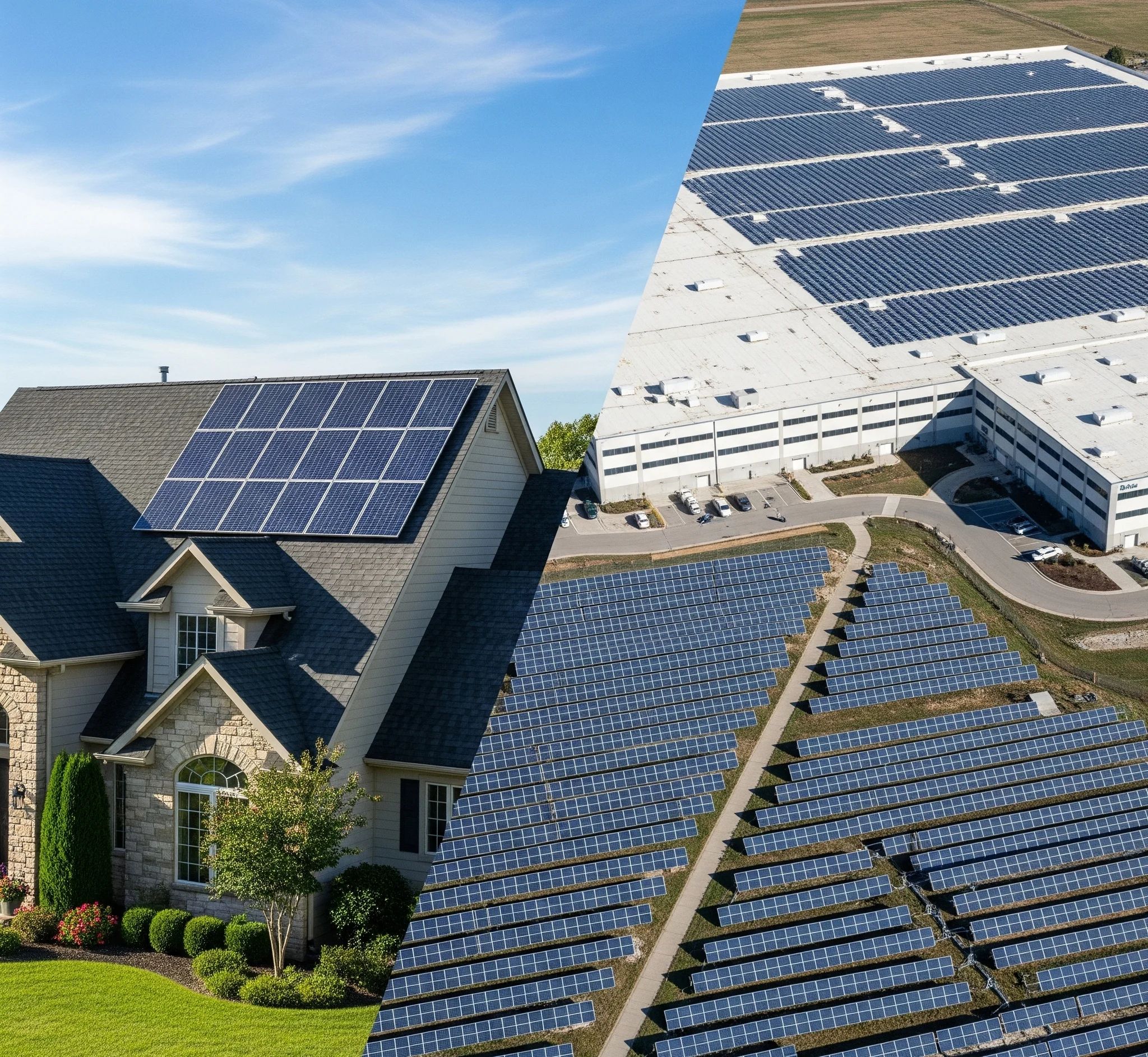

Residential Solar System Characteristics
-
System Capacity: The typical residential solar panel system is usually between 5–12 kilowatts to satisfy common household power use of 25–40 kilowatt-hours per day. They usually use 15–40 separate solar home solar panels with respect to the efficiency of the panel and the available roof area.
-
Installation Footprint: The residential systems operate under the confines of available roof space, where, in many cases, new and innovative placement solutions must be effective to provide as much potential energy production as possible without loss of aesthetics of installation. Orientation, shading, and architectural features of the roof are also important in the design of the system.
-
Energy Production Scale: On average, a housing solar system installation can produce between 6,000 and 15,000 kilowatt-hours/year, which is enough to eliminate or cover most or all of a home's power consumption in the best climate.
Commercial Solar System Characteristics
-
System Capacity: Commercial solar systems may be as small as 25 kilowatts and may scale as large as several megawatts, based on use by large industrial operations. Such systems can have hundreds or even thousands of industrial solar panels on several roof areas or ground-mounted arrays.
-
Installation Footprint: Solar for business applications benefits from ample commercial roof space, allowing flexible installations that maximize energy generation. The system is very flexible, with large flat roofs, parking facilities and specific areas on the ground next to each other..
-
Energy Production Scale: Commercial systems produce tens to millions of kilowatt-hours per year with power-generating units programmed to offset significant energy usage in business, to produce maximum cost advantage.
Residential vs Commercial Solar Panels: Side-by-Side Comparison
|
Feature |
Residential Solar Panels |
Commercial Solar Panels |
|---|---|---|
|
System Size |
3 – 10 kW |
50 kW – MW range |
|
Panel Size |
Smaller (60-cell) |
Larger (72-96 cell) |
|
Efficiency |
Moderate (15–20%) |
Higher (17–22% or more) |
|
Installation Type |
Rooftop on sloped residential roofs |
Flat rooftops, ground-mounts, carports |
|
Aesthetic Consideration |
High (blend with home design) |
Lower (focused on performance) |
|
Cost per Watt |
Slightly higher due to scale |
Lower with economies of scale |
|
Maintenance |
Minimal |
Requires monitoring for larger setups |
|
Incentives & Subsidies |
Residential solar tax credits & subsidies |
Commercial solar depreciation & rebates |
Equipment and Technology Differences
Panel Specifications and Performance
-
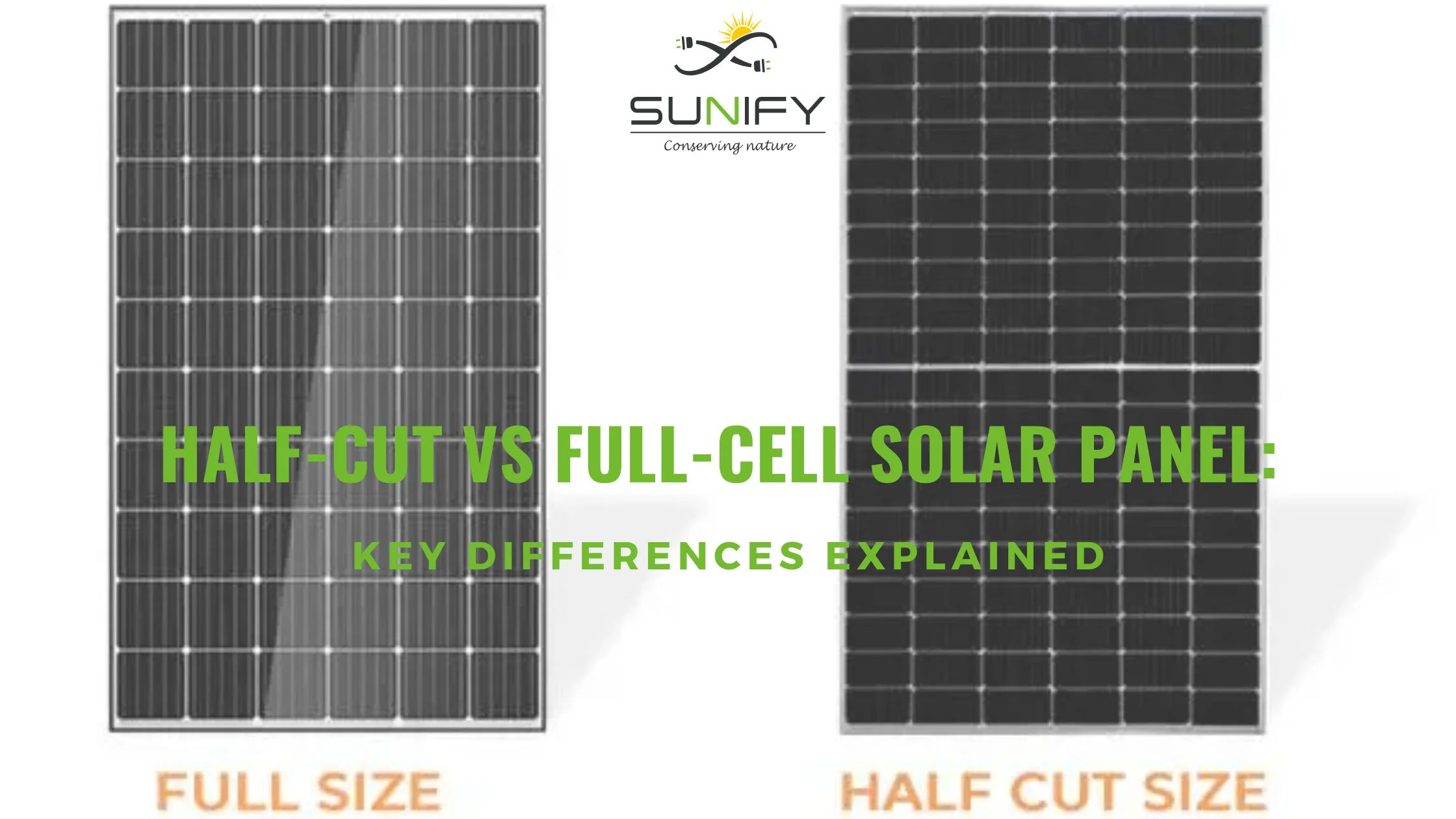
Residential Solar Panel Technology: The 2 common panel types installed in homes are the 60-cell and 72-cell panels, producing an average of 300–400 watts per panel. House solar panels today are also designed with aesthetics in mind, featuring black frames and sleek surfaces to blend with rooftops.
-
Commercial Solar Panel Technology: In contrast, commercial solar panels often use 72-cell or 144-cell bifacial panels producing 400–600+ watts, aimed at maximizing output. These systems prioritize cost-efficiency and output over aesthetics..
Inverter Systems and Electrical Infrastructure
-
Residential Inverter Solutions: Typical home panel solar systems include string inverters, power optimizers, or microinverters are mutually exclusive measures that are most often implemented in home systems, depending on the complexity of the roof and shading. These are systems that are compatible with the residential electrical panels of 200-400 amps.
-
Commercial Inverter Solutions: In business installations, larger-sized string inverters or central inverters that can process a higher voltage and power are used. Greater flows of energy are facilitated by three-phase electricity and dedicated commercial electrical infrastructure.
Monitoring and Control Systems
-
Residential Monitoring: Home systems feature simple monitoring systems with emphasis on energy generation, consumption, as well as alerting on the performance of the system. The homeowner is a priority in user interfaces; it is simple, and they are user-friendly.
-
Commercial Monitoring: Business systems take the form of advanced monitoring and control systems that give detailed performance analytics, predictive maintenance, and integration with building management systems.
Installation Process Variations
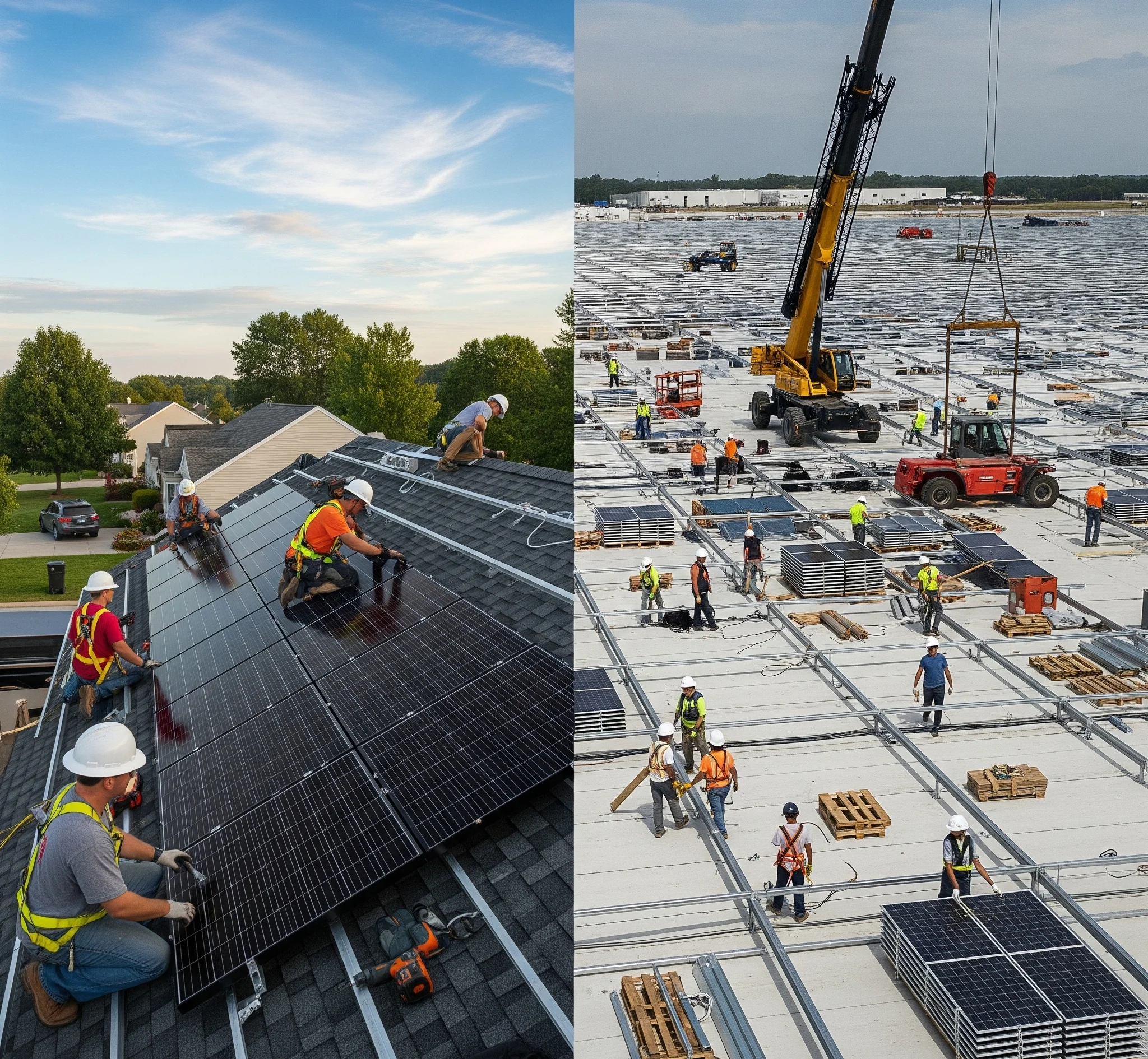

Residential Installation Considerations
-
Permitting and Approvals: Residential solar installation requires standard building permits and utility interconnection agreements, typically processed within 2-6 weeks depending on local jurisdiction requirements.
-
Structural Requirements: Home installations must consider roof age, structural integrity, and weight capacity. Most residential roofs accommodate solar panels without structural modifications, though professional assessments ensure safety and compliance.
-
Installation Timeline: Residential projects typically complete within 1-3 days of actual installation work, though total project timelines including permitting and inspections may extend 2-4 months.
Commercial Installation Considerations
-
Complex Permitting Process: Commercial solar installation involves more extensive permitting requirements, including detailed structural engineering, electrical studies, and environmental assessments. Approval processes may extend 3-12 months for large installations.
-
Structural Engineering: Commercial installations require comprehensive structural analysis and often involve reinforcement or modification of existing roof systems. Large installations may require specialized structural support systems.
-
Extended Installation Timeline: Commercial projects can require weeks or months of installation work depending on system size and complexity. Project coordination with ongoing business operations adds additional scheduling considerations.
Maintenance and Operational Differences
Residential System Maintenance
-
Homeowner Responsibilities: Residential systems require minimal maintenance beyond occasional cleaning and basic visual inspections. Most home solar systems owners can perform routine maintenance tasks or arrange for periodic professional service.
-
Service Requirements: Home installations benefit from standardized equipment and widespread service networks, ensuring readily available maintenance and repair services at competitive costs.
Commercial System Maintenance
-
Professional Maintenance Programs: Commercial installations typically require structured maintenance programs including regular inspections, cleaning, and performance optimization. Professional maintenance ensures maximum energy generation and system longevity.
-
Advanced Monitoring Needs: Business systems utilize sophisticated monitoring to identify performance issues, schedule preventive maintenance, and optimize energy production throughout the system's operational life.
Future Considerations and Expansion
Contact Today For Your Solar Needs
Residential System Evolution
-
Technology Integration: Home solar systems increasingly integrate with battery storage, electric vehicle charging, and smart home energy management systems.
-
Expansion Limitations: Residential systems face physical limitations for expansion of commercial solar systems, making initial sizing decisions crucial for long-term satisfaction.
Commercial System Evolution
-
Scalability Advantages: Commercial installations offer greater flexibility for future expansion as business needs evolve or additional installation areas become available.
-
Advanced Integration: Business systems can integrate with sophisticated building management systems, energy storage solutions, and demand response programs.
Sunify Solar – Future-Ready Solar Panels
For future-proof solar solutions, Sunify Solar stands out as a trusted solar panel manufacturer in India, offering high-efficiency monofacial and bifacial solar panels. Their advanced systems are ideal for all use cases - residential solar panel needs, housing solar system rooftops, commercial facades, and ground-mounted arrays, ensuring maximum energy output. and seamless integration with evolving solar technologies. With innovation, sustainability, and long-term reliability, Sunify Solar empowers users with solar home solar panels ready for evolving energy needs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solar Solution
The difference between home and enterprise solar courses go far beyond the measurement of size. Any of these types of systems is specially designed to address the various demands of energy generation, the environment where the system is installed, the budgetary considerations, and the working requirements.
We are ahead as outlined by the residential solar systems providing sustainable energy solutions to the homeowners that fit into the already established infrastructure, as well as long-term affordability and environmental implications.
Businesses can reduce their energy costs dramatically, boost their sustainability credentials, and produce appealing returns on investment by increasing the size of the off-take as well as hiring professionals to run them, with commercial solar installations.
By being aware of the major differences between residential and commercial solar, by looking at the angles that affect each of solar and how they might influence the real estate identities and how these aspects can work out favorably with the property owners, a correct decision will be made in accordance to the nature in which an individual needs to run their property as well as their financial goals and operation needs. In both residential and commercial solar installation, the anyone-can-do-it sentiment should be discouraged because the presented experiences do not make an optimal system design structure and yield its maximum long-term advantages.
Recently Posted
Whatsapp Chatx
Hi! Click one of our representatives below to chat on WhatsApp or send us email to solar@sunifysolar.in

|
************** +91 81414 55503 |

We will love to hear from you!