Connect With Our Team
With the ever-growing global demand for renewable energy, selecting the proper solar PV panels plays a key role in gaining the most efficient and cost-effective use of solar energy and maintaining long-term performance. One of the most talked-about comparisons in the solar industry today is the half cut panel versus the full-cell solar panel. While both serve the same purpose—converting sunlight into electricity—their design, performance, and cell structure differ significantly. This guide explores their core differences, applications, and real-world benefits.
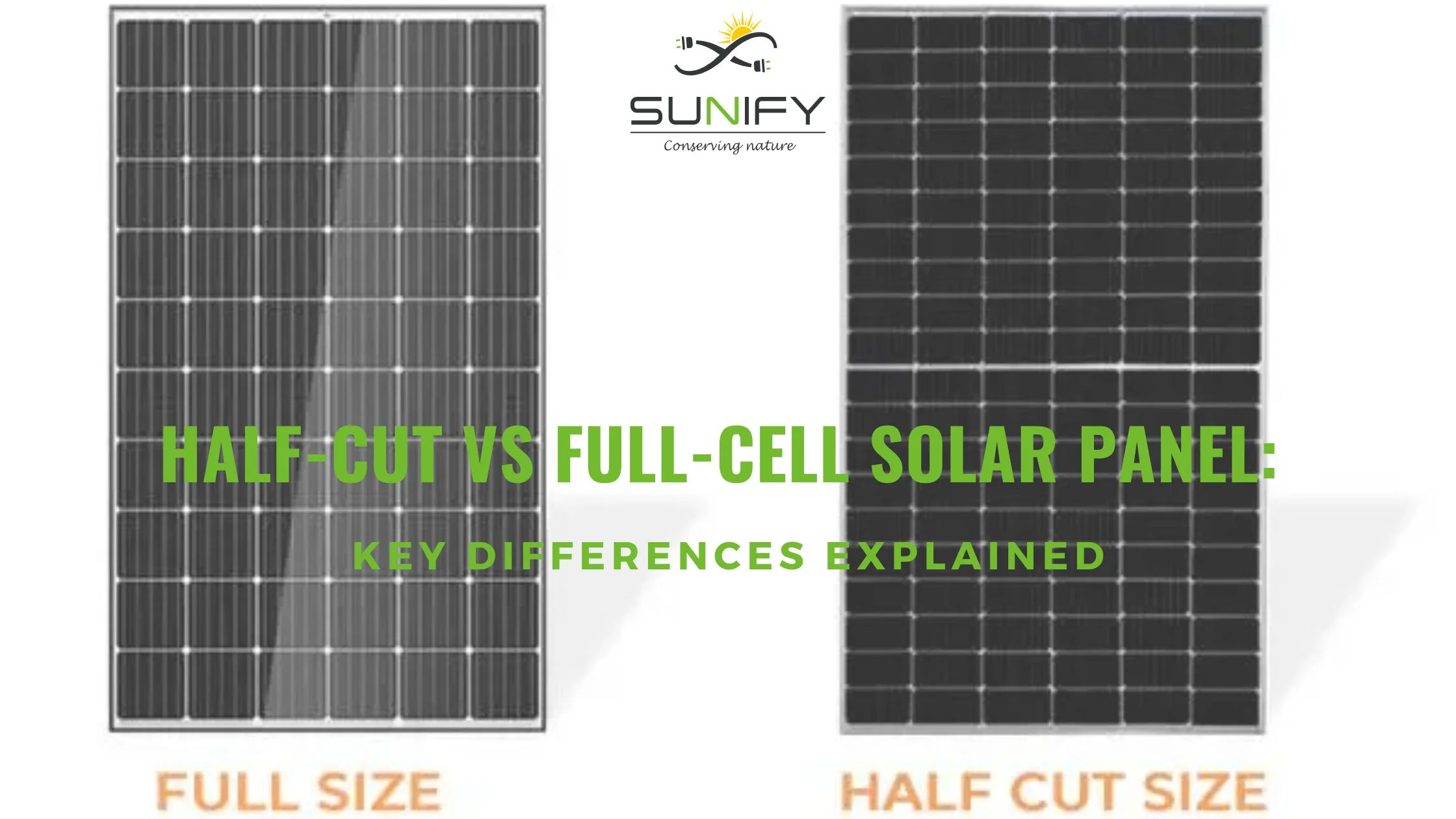
What Are Full-Cell Solar Panels?
Traditional or standard solar PV panels are known as full-cell solar panels. These panels are composed of photovoltaic (PV) cells arranged in a structured layout, typically 60 or 72 full-size cells made from crystalline silicon. Since they represent mature technology, they’re widely manufactured and come at a lower cost.
They perform reliably in direct sunlight and are widely used in large-scale solar farms, industrial rooftops, and locations with minimal shading. However, they’re prone to efficiency drops due to partial shading, micro-cracks, and overheating over time.
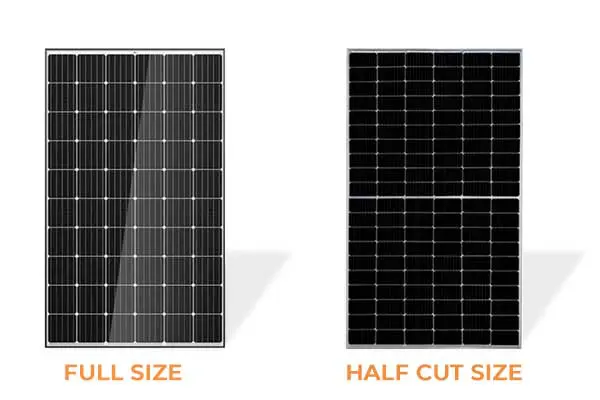

What Are Half-Cut Solar Panels?
A more advanced design, solar panel half cut technology, involves slicing traditional full-size cells in half using laser techniques. This creates twice the number of cells in a panel usually 120 or 144, which helps lower the current per cell, ultimately minimizing resistive losses and improving efficiency.
Modern half cut solar panels are built with two independent strings of cells, which ensures that if one half is shaded, the other half continues to generate electricity. This makes them ideal for urban rooftops, commercial buildings, and shaded environments. Many of these also use half cut mono PERC solar panel technology to further enhance efficiency and thermal performance.
Benefits of Half-Cut Solar Panels
-
Higher Efficiency: Reduced resistance in each half cut solar cell leads to better energy conversion.
-
Improved Shading Performance: Dual strings ensure power generation continues even if one portion is shaded.
-
Better Heat Tolerance: Reduced heat buildup allows for higher performance in warm climates.
-
Lower Power Loss: Minimal resistive losses due to lower current per cell.
-
Greater Durability: Better resistance to mechanical stress enhances longevity.
-
Optimized for Space: Great for areas where space is limited but high output is needed.
Half-Cut vs Full-Cell Solar Panels: A Detailed Comparison
| Feature | Full-Cell Panels | Half-Cut Panels |
| Cell Structure | 60 or 72 full-size cells | 120 or 144 half cut solar |
| Efficiency | Moderate | Up to 2–3% higher due to improved design |
| Shading Tolerance | Low – shading impacts the entire module | High – independent strings continue energy production |
| Heat Resistance | Average | Better – minimal heat accumulation |
| Durability | Prone to cracks | Improved stress resistance |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Slightly higher, but better long-term ROI |
| Power Output | Sufficient for basic needs | Higher yield under similar conditions |
Real-World Performance in Different Conditions
When tested in diverse conditions, half-cell solar panel designs show superior results. The reduced current per cell minimizes internal heating, making them more efficient in hotter regions. Also, because of their split and parallel wiring, shading on a portion of the module only affects that section, unlike traditional full-cell panels, where one shaded cell can reduce output drastically.
Though full-cell panels are more affordable at the start, their performance declines faster in partially shaded areas, making half-cut panel technology more suitable for urban or variable-light environments.
Manufacturing Process & Cost Considerations
Full-cell solar PV panels are simpler and more cost-effective to produce, making them ideal for large-scale, budget-sensitive projects. However, their energy yield can be lower in real-world scenarios with variable sunlight or heat.
Solar panel half cut technology, despite slightly higher manufacturing costs due to laser cutting and added soldering, provides better efficiency, longer life, and lower transmission loss. Over time, these benefits offset the initial price difference, especially for installations that demand consistent performance.
Applications & Benefits
1. Half Cut Solar Panels:
-
Urban Homes & Apartments: High performance in shaded and hot environments.
-
Commercial Buildings: Better ROI and consistent power supply.
-
Off-Grid Installations: Reliable in rural or remote setups.
-
Hot Climate Zones: Lower heat-induced losses.
2. Full-Cell Solar Panels:
-
Utility-Scale Projects: Cost-effective for large, open installations.
-
Industrial Roofs: Affordable and suitable for wide-area coverage.
Which Solar Panel Should You Choose?
Your ideal panel depends on your project’s environment, budget, and energy expectations.

Choose Half Cut Panels If:
-
Partial shading is a factor
-
You operate in a hot or tropical region
-
You want higher efficiency and reliability
-
Long-term returns matter to your project
Choose Full-Cell Panels If:
-
You have ample unshaded space
-
You require a lower upfront investment
-
You're managing a large-scale, cost-driven installation
Conclusion: Making the Smart Solar Choice
Both full-cell and half cut solar panel technologies have their strengths. While full-cell options are perfect for controlled, open-field conditions, half cut mono PERC solar panel technology is quickly becoming the industry standard due to its improved efficiency, durability, and overall performance.
Looking for Reliable Solar Panel Solutions?
Partner with Sunify Solar LLP - a trusted manufacturer and exporter of high-quality half cell solar panel solutions including monofacial and bifacial half-cut solar modules. With a commitment to innovation and client satisfaction, Sunify delivers certified, durable, and highly efficient solar PV panels tailored for domestic, commercial, and industrial applications.
Sunify Solar LLP offers expert guidance and custom solar solutions to help you invest in a greener, smarter, and more sustainable future.
Recently Posted
Whatsapp Chatx
Hi! Click one of our representatives below to chat on WhatsApp or send us email to solar@sunifysolar.in

|
************** +91 81414 55503 |

We will love to hear from you!