Connect With Our Team
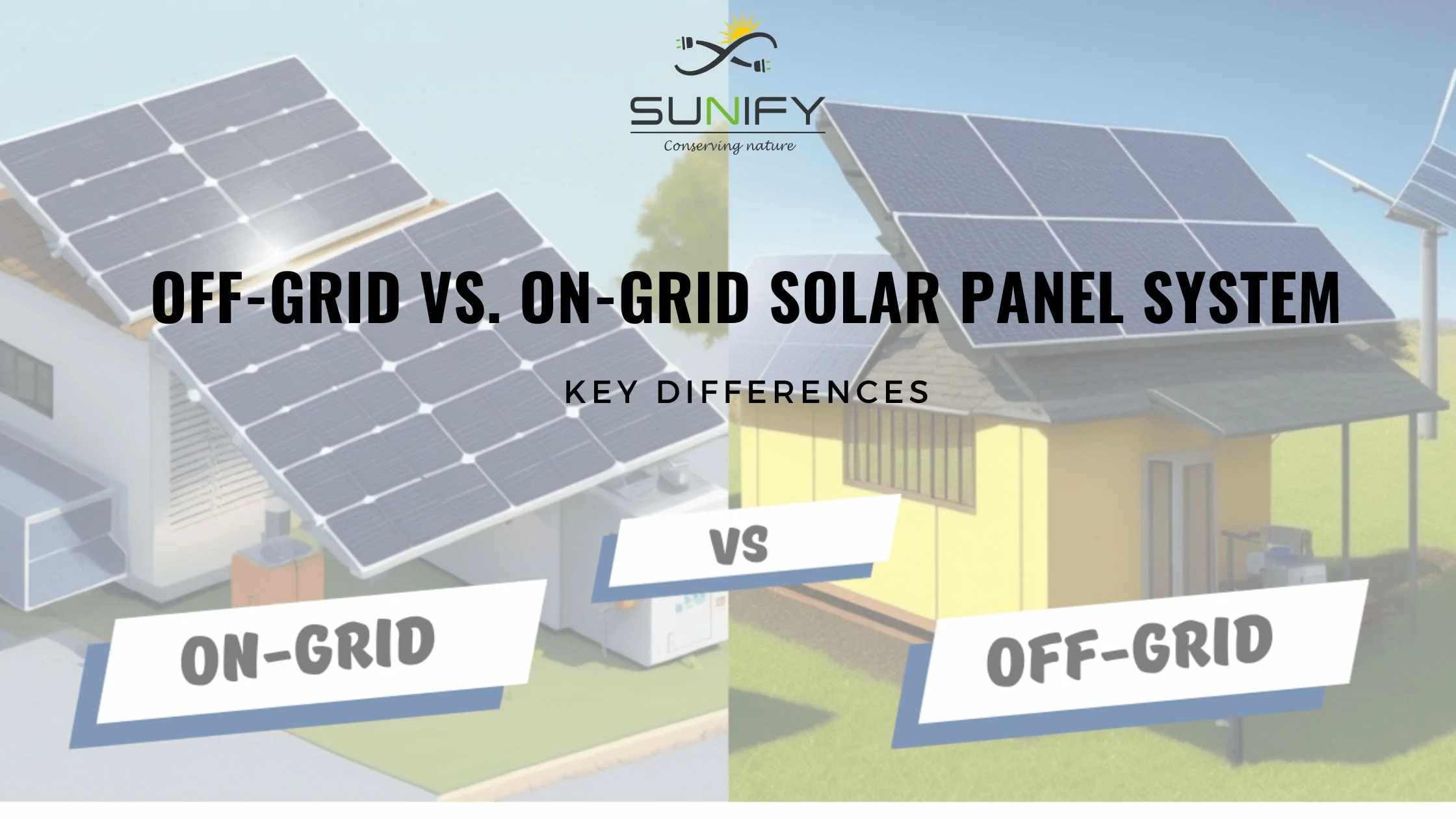
As solar energy adoption rises globally, one of the most critical decisions for homeowners and businesses is whether to install an on-grid or off-grid solar panel system. Both systems convert sunlight into electricity, but they operate differently and suit different energy needs. In this article, we will explore the key differences between these systems to help you make an informed decision.
What is an On-Grid Solar System?
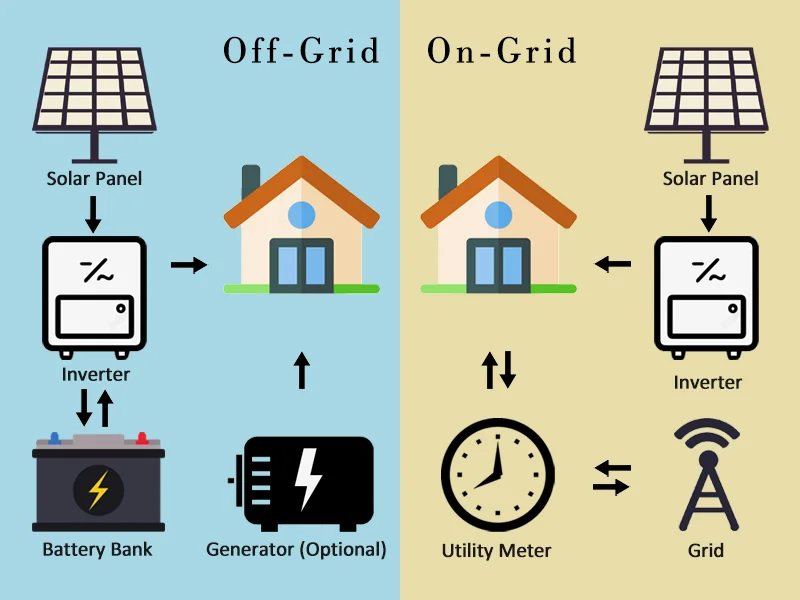
On-grid is also referred to as grid-tied, grid-connected, or works with the local power network. In such a solar system, if there happens to be excess electricity produced by a solar panel that hasn't been put into use yet, such energy will therefore feed back into the electricity mains. This credits the owner of the system by a technique called net metering.
On-grid systems rely on the grid for supplemental power at times when they cannot generate electricity, for example during nightfall and cloudy days, making it a more practical and applicable solution for urban and suburban use where one is assured of a stable and readily available grid.
What is an Off-Grid Solar System?
The off-grid solar system is not connected to the utility grid. So it is a totally self-contained source of energy and, thus, all the electricity it produces is utilized within the system itself. A consistent power supply, particularly when production levels from the solar system are at their lowest, is achieved in off-grid systems by storing excess energy produced for later use in the form of batteries.
This kind of system is very popular off the grid, especially for areas that cannot be easily reached by the grid or with people who look forward to having complete control over their energy supplies. Off-grid systems, however, are considered more complex, so they come at a higher upfront cost on account of additional components such as battery banks, charge controllers, and inverters.
1. System Connectivity
-
Off-Grid System: This is a system that operates completely independently of the electrical grid. Therefore, it requires batteries to store extra energy for any extra usage and supply, when the sun is not shining, which will ensure that you have power all the time even in case of a blackout or in remote areas.
-
On-Grid Solar System: These are known as grid-tied systems; their operation actually depends majorly on the local electrical grid. They will use no batteries because the excess generated energy would be fed back into the grid, and you can draw all the power you need from the grid.
2. Energy Storage
-
Off-Grid: In off-grid systems, that do not connect to the utility grid, dependency relies more on battery storage. It means you will have enough battery capacity for the storage of energy that is captured in the day for use at night or when sunlight is low in intensity. Off-grid systems can be costly because the front-end cost of batteries.
-
On-Grid: On-grid systems rarely require batteries to operate since you're essentially using the grid itself as a "virtual battery." Excess energy generated by your solar panels feeds back into the grid, and through the process of net metering, you may see credits going onto your account. You can draw electricity from the grid when your production is low.
3. Cost and Affordability
-
Off-Grid: The initial cost is a little more offsetting as they seem to demand more equipment-the batteries and more advanced inverters, for instance. While offering independence completely from the grid, that extra investment would better be spent on very remote places where accessing the grid could be challenging or expensive.
-
On-Grid: On-grid systems are typically more economical since they have fewer parts. With on-grid systems, you can also take net metering programs wherein the cost of electricity generated is balanced out by producing back to the grid, thus reducing the bills. Therefore, on-grid systems are the most suitable for towns and cities with easy access to a grid.
4. Energy Independence
-
Off-Grid: The greatest advantage that an off-grid system has is complete independence of energy supply. You do not rely on the local utility company for power-this means you can continue operating in case of a grid failure or blackout. Off-grid systems are ideal for remote locations, like a rural home, cabin, or some location where grid access is limited or unavailable.
-
On-Grid: In an on-grid system, you are still reliant on the electrical grid for a stable and consistent power supply. You can potentially lower or even eliminate your electricity bill, but your system will not be working in the event of a power outage unless you have a battery backup installed. This is simply because it automatically shuts down in order not to have electricity sent back into the grid to prevent safety hazards for utility workers.
5. Maintenance and Reliability
-
Off-Grid: Because off-grid solar systems require maintenance, especially of the batteries, the life cycle of a battery ranges from 5 to 15 years depending on the product type, and replacing them becomes costly. Energy independence maintenance also involves monitoring the energy consumed. You should ensure that you are not overusing power stored in the battery more than you should.
-
On-Grid: Compared to an off-grid, an on-grid system solar system tends to require less maintenance. Since your household is attached to the power grid, you don't depend much on the backup of your batteries and therefore use them less frequently. In any case, if you do install battery backup, that's a different story.
6. Environmental Impact
-
Off-Grid: The off-grid systems, on the other hand, encourage self-sustenance and are, therefore, environmentally friendly. On the other hand, you might need big batteries, which is considered bad for the environment, containing terrible chemicals that could have disastrous side effects in the long run.
-
On-Grid: on-grid systems reduce your carbon footprint through the use of renewable energy. Through net metering, any extra power that you generate helps supply clean energy to other homes and businesses, maximizing the benefits of environmental friendliness during your installation.
| Features | On-Grid Solar System | Off-Grid Solar System |
| Connection | Connected to the utility grid | Independent of the utility grid |
| Energy Independence | Partial – relies on the grid when solar power is insufficient | Complete energy independence, no reliance on the grid |
| System Components | Solar panels, inverter, net metering system | Solar panels, inverter, battery storage, charge controller |
| Battery Storage | Not required, optional for hybrid systems | Essential for energy storage and backup |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost due to no need for batteries | Higher upfront cost due to battery and extra components |
| Electricity Bills | Reduced or eliminated bills through net metering | No electricity bills but ongoing costs for battery maintenance |
| Grid Dependence | Dependent on the grid for backup power. | Completely independent from the grid |
| Scalability | Easy to scale by adding more panels or upgrading components | More difficult and expensive to scale, requires more batteries |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces carbon footprint but relies on the grid when solar isn’t available | Fully sustainable, but batteries can have environmental impact |
| Urban vs. Rural | Ideal for urban and suburban areas with reliable grid access | Best for rural or remote areas with no grid access |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, panels need occasional cleaning, the inverter may need replacement | Higher maintenance due to battery upkeep and eventual replacement |
| Power Reliability | Relies on grid stability; no power during outages without battery backup | Independent of the grid; continuous power with proper battery management |
| Net Metering | Excess energy is fed into the grid for credits | Not applicable, all generated energy is stored and used on-site |
| Government Incentives | Eligible for various tax credits and rebates | May have fewer incentives but still qualify for renewable energy rebates |
| Installation Complexity | Simpler installation, fewer components needed | More complex installation due to battery integration |
The Best in Solar: Exploring the Top Brand of Solar Panels
The Sunify Solar LLP, being one of the top manufacturers and suppliers of monofacial and bifacial solar panels, is positioned as high-tech and sustainable. It acts as one of the massive corporations promising to cater efficiently to diverse energy needs by taking care to provide maximum efficiency and durability. A product portfolio from one-sided monofacial solar panels that capture the sun's rays on one side to two-sided bifacial panels generating power on both sides is available at Sunify Solar, maximizing energy production suited for residential, commercial, and industrial applications for use all over the world.
Conclusion
The choice between an off-grid or on-grid solar panel depends on location, budget, energy needs, and the degree to which one is comfortable being independent. Off-grid systems grant autonomy from the grid but are relatively expensive and demanding with regard to maintenance. On-grid systems are affordable, convenient, and easily applicable to an urban scenario, with the benefits of net metering, and maintenance costs are less.
Recently Posted
Whatsapp Chatx
Hi! Click one of our representatives below to chat on WhatsApp or send us email to solar@sunifysolar.in

|
************** +91 81414 55503 |

We will love to hear from you!