Connect With Our Team
When evaluating energy options for your home or business, the cost comparison between solar power and traditional energy has become one of the most critical financial decisions property owners face today. The landscape of solar vs traditional energy costs has transformed dramatically, with solar installations now offering compelling economic advantages that extend far beyond simple monthly bill reductions.
The Real Cost of Traditional Energy
Traditional energy costs encompass much more than the monthly electricity bill that arrives in your mailbox. The typical household in the United States consumes electricity at an annual expenditure of 1,500 - 2500 dollars and the cost depends greatly on the region and usage patterns. Nevertheless, these monetary expenses are not even a quarter of the actual financial implication of using conventional power grid electricity.
The cost of utilities has been steadily rising in the last 20 years and the residential electricity prices have been advancing at a rate of around 2.5% in the record. This incremental increase will imply that a family currently paying 150 dollars a month on electricity will pay more than 200 dollars a month in a decade, provided growth in the rise of rates remains constant. Over 25 years, the cumulative cost of traditional electricity for an average household can easily exceed $60,000–$80,000.
Peak demand charges and time-of-use rate structures add additional complexity to traditional energy costs, particularly for commercial users. Most utility companies employ tiered rates whose high usage penalizes peak times, offering highly variable monthly electricity bills that may entirely change depending on both usage habits and seasonal needs.
The hidden costs of traditional energy include infrastructure maintenance fees, distribution charges, and regulatory compliance costs that utilities pass on to consumers through base rate adjustments. Such costs keep mounting whether households use electricity or not making them have fixed costs which can never be eliminated even when households strive to minimize their electrical use.
Solar Power Investment Analysis
Solar power costs operate on a fundamentally different financial model that shifts from ongoing monthly expenses to a one-time capital investment followed by decades of free electricity generation. Modern solar installation setups for residential use typically cost $15,000–$30,000 before incentives, though federal tax credits and state rebates often reduce net costs to $10,000–$20,000 for most homeowners.
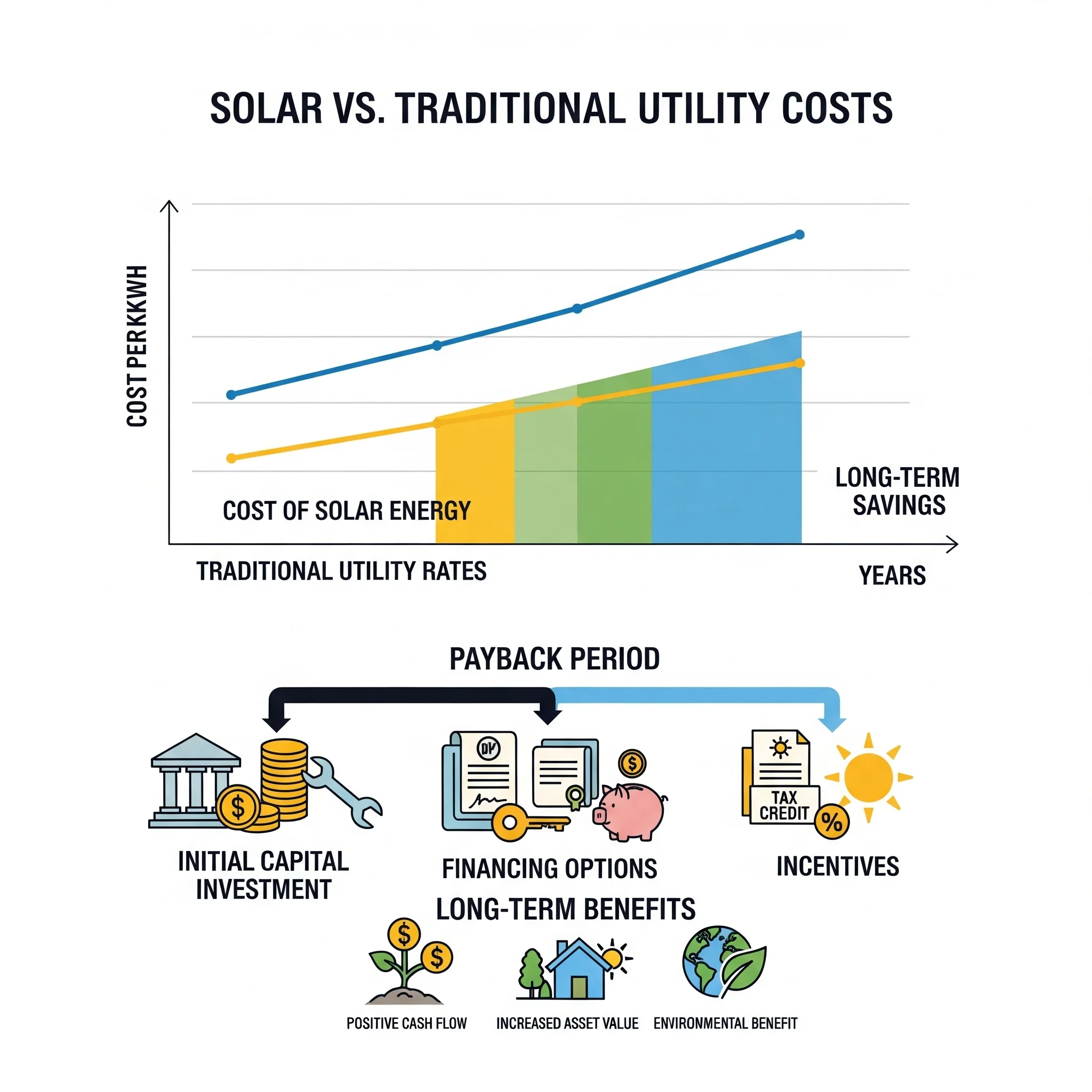
The solar energy cost per kilowatt-hour over the system's 25–30 year lifespan typically ranges from $0.05–$0.10, significantly below current utility rates in most markets. This calculation entails all the initial expenses, the costs of financing, maintenance needs, and replacement of equipment over the entire life of the system in use.
Solar financing options have evolved to eliminate upfront cost barriers for homeowners and businesses. Solar companies now offer loans with favorable terms enabling immediate positive cash flow, where monthly loan payments often cost less than the electricity bill savings generated by the home solar system. This form of financing lets the property owners start saving money as soon as possible as they create a stake in owning a highly valued energy asset.
Leasing finance and the power purchase agreement proposals offer options to consumers who do not wish to make any upfront investment. Although total-cost savings, in the long term, can be lower than ownership, savings in electricity costs of 1030% can be achieved with zero outlays upfront.
Geographic Cost Variations Create Different Economics
The economics of solar power vs traditional energy vary significantly across different geographic markets, creating diverse investment scenarios for property owners. High electricity rate markets such as California, Hawaii, Connecticut, and Massachusetts offer exceptional solar energy value propositions due to expensive traditional energy costs combined with abundant solar incentives.
California residential customers paying $0.25–$0.35 per kilowatt-hour can achieve solar panels for home payback periods of 5 - 7 years, followed by nearly two decades of free electricity. Hawaii’s extreme electricity rates, often exceeding $0.40 per kilowatt-hour, create even more dramatic solar energy savings opportunities with payback periods under five years.
Moderate electricity rate markets throughout the southeastern and midwestern United States still provide attractive solar power economics, though payback periods may extend to 8–12 years. Even in markets with relatively low electricity rates, solar panels for your home typically generate positive returns over their operational lifespans.
The availability of solar resources has implications for the system design and economic stability, where southwest markets have 50-80 percent more annual sunshine compared to the northern part. However, excellent solar installation economics exist even in moderate solar resource areas due to improved technology efficiency and favorable net metering policies.
Commercial and Industrial Cost Considerations
Commercial solar installations benefit from economies of scale that significantly improve project economics compared to residential systems. Large commercial solar installation projects often achieve per-watt costs 30–50% below residential pricing while qualifying for accelerated depreciation benefits that provide substantial tax advantages.
One of the greatest commercial solar advantages that is easily missed in an apples-to-apples cost analysis is demand charge management. Most companies pay sizable monthly demand charges driven by the maximum power consumption, which can be up to 30-50 percent of whole electricity expenditure. Solar installations reduce these expensive demand charges by providing power during peak consumption periods.
Commercial electricity rates frequently include complex time-of-use structures that align well with solar energy generation patterns. Peak rate periods during midday hours coincide with maximum solar power production, maximizing the value of every kilowatt-hour generated.
Industrial facilities with high energy consumption achieve exceptional returns from large solar energy installations due to substantial electricity cost offsets and favorable commercial financing terms. Manufacturing operations consuming millions of kilowatt-hours annually can realize solar power savings exceeding $100,000 per year.
Long-Term Savings of Solar Power vs Traditional Energy

Solar Power Savings
Once the installation is complete, solar power users experience significant long-term cost benefits.
-
Reduced Electricity Bills: Since solar panels generate electricity from sunlight, homeowners can dramatically lower or eliminate monthly utility payments. For example, a 6kW solar system in sunny regions can save around $1,200 annually in energy costs. As the sun is harnessed to supply electricity through a solar panel, monthly electricity bills can be immensely reduced or abolished by the house owner. As a case in point, a panel of 6kW in sunny areas can be able to cut costs by up to $1,200 yearly in energy expenses.
-
Net Metering: Many regions offer net metering, allowing you to sell excess energy generated back to the grid, providing additional savings. Most of the areas provide net metering where you can sell back the additional energy you have produced supplying you with extra savings.
-
Lifetime Cost Efficiency: With a useful lifespan of 25–30 years, solar panels pay for themselves multiple times over. Once the system’s upfront costs are recouped (usually within 6–9 years), the remaining years generate pure savings. As a 25-30 year investment, the solar panels pay themselves off several times. After the up front costs of the system are paid back (typically in 6-9 years), the years that follow are pure savings.
Example:
-
A homeowner who installs a 6kW system for $18,000:
-
After ITC (30%), net cost = $12,600
-
Annual energy savings = $1,200
-
System pays for itself in ~10 years
-
Total lifetime savings (20 years post payback) = $24,000+.
Traditional Energy Costs
-
Monthly Utility Costs: Fossil fuel-based energy costs fluctuate with global market factors, often rising over time. Average annual energy bills for a typical U.S. household can exceed $1,500. Fossil-fuel-based energy is subject to fluctuations in global markets and generally will continue to increase over time. The average yearly power bills for the typical U.S. residence may be more than $1,500 a year.
-
Energy Price Inflation: Historical data show that electricity rates increase yearly by about 2–5%, compounding financial burdens for long-term grid users. Over the years, historical data reveals that residual electric billing will increase annually between 2-5%, resulting thus an increasing financial burden to long term grid usage.
-
Dependence on Fossil Fuels: Non-renewable energy sources like oil, gas, and coal are finite, meaning their rising scarcity will likely continue driving costs higher. Renewable energy, such as oil, gas and coal, is non-renewable, which indicates that their increasing depletion is imminent, breakdown of the impending cost hike.
Takeaway:
While traditional energy incurs lower initial expenses, solar energy offers undeniable long-term savings, especially for users located in sunny regions with access to pricing incentives. Although traditional energy has cheaper costs of implementation, solar energy has inescapable cost advantages in the long particularly among the parties that utilize the energy in sunny areas and have access to pricing credits.
Long-Term Financial Projections Favor Solar
25-year cost analysis reveals the true economic advantage of solar power over traditional energy sources. A typical solar installation costing $20,000 after incentives will generate approximately $40,000–$60,000 in electricity bill savings over its operational lifetime, representing returns of 200–300% on initial investment.
Net present value calculations for solar power show positive returns even when accounting for financing costs and opportunity costs of capital investment. Quality monocrystalline solar panels with performance warranties provide predictable returns that exceed most conservative investment alternatives.
Conventional estimation on energy costs has indicated a further annual rise of 2-4 per cent, because of the need to modernize the infrastructure, environmental regulatory expenses, and unstable fuel prices. These increases in energy costs are multiplied over the years, forming more costly and expensive energy costs in the long-term perspective of the consumer using grid electricity.
Solar panels for house provide protection against future utility rate increases through predictable energy costs throughout the system’s operational life. Such price stability allows proper long-term financial planning by removing risks of being affected by the dynamic nature of energy markets.
Hidden Costs and Additional Benefits
Energy independence benefits protect home solar system owners from power outages and grid reliability issues while providing long-term cost predictability. Best solar generators and 12v solar panel solutions can provide complete energy independence during grid disruptions, adding substantial value beyond simple cost savings.
The benefits of energy independence ensure that the owners of home solar systems are not affected by power cuts or compromised grid reliability and offer predictability in terms of costs over the long term. The most savvy solar generators and 12v solar panel solutions, however, can ensure energy freedom in the event of grid down scenarios which in itself has greater value than just saving money.
Solar panels for the home benefit the environment by letting the house avoid the external costs of conventional energy production, such as air pollution, water consumption, and climate change effects. Although these advantages are not of direct financial benefit to individual households, they have high societal value that is not reflected in the costs of traditional energy.
The hidden costs of conventional energy are ecological externalities of the environment, grid reliability expenditure, and volatile fuel prices that may bring uncertain long-range costs to consumers. These expenses do not directly appear as bills each month, but they eventually trickle down to utility rates and the energy prices in the long term.
Making the Financial Decision
The cost comparison between solar power and traditional energy clearly demonstrates the financial advantages of solar panels for house for most residential and commercial applications. Although there is no initial investment in conventional energy, it is way more expensive than solar installations in most of the markets over a 20 to 25-year period.
Solar energy offers predictable long-term costs, protection against utility rate increases, and substantial return on investment through decades of free electricity generation. The combination of declining solar panels for your home costs, improving technology performance, and generous incentive programs creates compelling financial advantages for solar power adoption.
For property owners with suitable installation conditions, solar power represents a superior long-term investment that delivers both immediate cost savings and substantial returns over the system’s operational lifespan. The financial advantages of solar power continue improving as types of solar panels evolve, technology costs decline, and traditional energy costs increase, making current market conditions ideal for solar power investment decisions.
Closing Insight
While solar power requires higher upfront investment, its long-term financial returns, environmental benefits, and low operating costs make it the better choice over traditional energy sources. With government incentives and financing options, adopting solar power is more achievable than ever.
When sustainability, savings and future proofing your energy demands are of importance, then solar is a long-term investment that will pay back many decades ahead.
Recently Posted
Whatsapp Chatx
Hi! Click one of our representatives below to chat on WhatsApp or send us email to solar@sunifysolar.in

|
************** +91 81414 55503 |

We will love to hear from you!